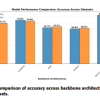
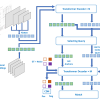
Understanding information extracted from receipts is a critical task for real-world applications such as financial tracking, auditing, and enterprise resource management. In this paper, we introduce ReceiptQA, a novel large-scale dataset designed for receipt understanding through question-answering (QA). ReceiptQA contains 171,000 question–answer pairs derived from 3500 receipt images, constructed via two complementary methodologies: (1) LLM-Generated Dataset: 70,000 synthetically generated QA pairs, where each receipt is paired with 20 unique, context-specific questions. These questions are produced using a state-of-the-art large language model (LLM) and validated through human annotation to ensure accuracy, relevance, and diversity. (2) Human-Created Dataset: 101,000 manually crafted questions spanning answerable and unanswerable queries. This subset includes carefully designed templates of varying difficulty (easy/hard) to comprehensively evaluate QA systems across diverse receipt domains. To benchmark performance, we evaluate leading vision–language models (VLMs) and language models (LMs), including GPT-4o, Phi-3B, Phi-3.5B, LLaVA-7B, InternVL2 (4B/8B), LLaMA-3.2, and Gemini. We further fine-tune a LLaMA-3.2 11B model on ReceiptQA, achieving significant improvements over baseline models on validation and test sets. Our analysis uncovers critical strengths and limitations of existing models in handling receipt-based QA tasks, establishing a robust benchmark for future research.
Research Date
Research Department
Research Journal
Mathematics
Research Member
Research Publisher
MDPI
Research Vol
13
Research Website
https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111760
Research Year
2025
Research_Pages
20
Research Abstract